Background
In KEGG, diseases are viewed as perturbed states of the molecular network system. Genetic and environmental factors of diseases, as well as drugs, are considered as perturbants to this system. Different types of diseases, including single-gene (monogenic) diseases, multifactorial diseases, and infectious diseases, are all treated in a unified manner by accumulating such perturbants and their interactions.
Current statistics (2024/4/25)
| KEGG DISEASE entries (H numbers) | 2,726 |
| H numbers with disease genes | 2,186 |
| Unique disease genes | 4,863 |
| H numbers with network variation maps | 747 |
| Unique network variation maps | 114 |
| H numbers with disease pathway maps | 75 |
| Unique disease pathway maps | 70 |
Our knowledge of perturbed molecular networks has been captured and represented as disease pathway maps in the KEGG PATHWAY database for a limited number of diseases. Efforts are now made to accumulate knowledge of various diseases and various perturbations in the KEGG NETWORK database represented as network variation maps.
KEGG DISEASE Database
KEGG DISEASE is a collection of disease entries, each containing a list of human disease genes and/or pathogens. The details of how molecular networks are perturbed by such perturbants are represented as network variation maps in the KEGG NETWORK database. KEGG DISEASE used to contain environmental factors, but they are now included only in KEGG NETWORK when molecular level information is available. Each disease entry is identified by the H number and may contain the link to network variation maps (see, for example, the disease entry of spinal muscular atrophy H00455). Therapeutic drugs are shown in the Drug field; those indicated in the FDA drug labels appear in the English version and those indicated in the Japanese drug labels appear in the Japanese version.
Disease entries are classified in the following BRITE hierarchy files.
Disease entries are classified in the following BRITE hierarchy files.
Network Variation Maps
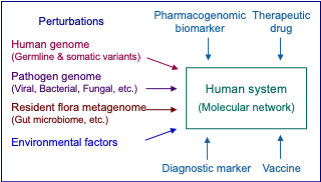
Network variation maps in the KEGG NETWORK database are a realization of the concept shown in the figure above. They indicate how perturbants, including human gene variants, viral and other pathogenic proteins and environmental factors, affect reference molecular networks (colored in green) and are associated with various diseases.
Disease Pathway Maps
The Human Diseases category of the KEGG PATHWAY database is a collection of disease pathway maps.
It contains multifactorial diseases such as cancers, immune system diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic diseases where known disease genes are marked in red. It also contains infectious diseases where interacting molecular networks of both pathogens and humans are depicted.
Disease Mapping
The KEGG Mapper Search tool with "hsa" mode contains a feature to search against disease genes accumulated in KEGG DISEASE entries, together with related KEGG pathway maps. The user may upload a set of human genes or KOs to check if any diseases may be associated with the dataset.
Pathway/Brite mapping of disease genes and drug targets
Disease genes accumulated in the KEGG DISEASE database and drug targets stored in the KEGG DRUG database are often represented in the KEGG PATHWAY and BRITE databases as well. The pathway maps and BRITE hierarchy files with mapping of disease genes and drug targets are identified by the five-letter organism code "hsadd" and the extension code "_dd", respectively.
For example, hsadd04620 represents disease/drug mapped toll-like receptor signaling pathway with the coloring convention as follows:
Pathway/Brite mapping of disease genes and drug targets
Disease genes accumulated in the KEGG DISEASE database and drug targets stored in the KEGG DRUG database are often represented in the KEGG PATHWAY and BRITE databases as well. The pathway maps and BRITE hierarchy files with mapping of disease genes and drug targets are identified by the five-letter organism code "hsadd" and the extension code "_dd", respectively.
For example, hsadd04620 represents disease/drug mapped toll-like receptor signaling pathway with the coloring convention as follows:
- When the gene is associated with a disease, it is marked in pink.
- When the gene (product) is a drug target, it is marked in light blue.
- When the gene is both a disease gene and a drug target, its coloring is split into pink and light blue.
Disease Classification
The following international standards are utilized in KEGG.
Last updated: January 26, 2024
