KEGG Overview
1. Genomes to Biological System
KEGG is a database resource for understanding high-level functions and utilities of the biological system, such as the cell, the organism and the biosphere, from genomic and molecular-level information. It is a computer model of the biological system, consisting of molecular building blocks of genes and proteins (genomic information) and chemical substances (chemical information) that are integrated with molecular wiring diagrams of interaction and reaction networks (systems information). The KEGG model also contains disease and drug information (health information) in terms of perturbed molecular networks.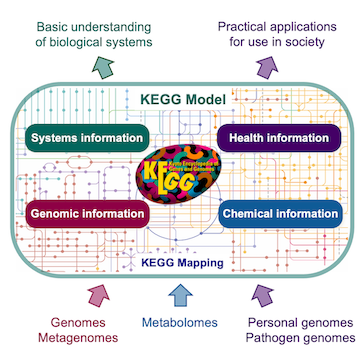
2. The KEGG Database
The KEGG model is realized by a collection of biological objects, called KEGG objects, for representation of both generic and human-specific biological information systems, which are implemented in sixteen databases shown below. They are broadly categorized into systems information, genomic information, chemical information and health information, and are distinguished by color coding of web pages.| Category | Model | Database | Object | Color |
| Systems information |
Biological information system |
PATHWAY | KEGG pathway maps | |
| BRITE | BRITE hierarchies and tables | |||
| MODULE | KEGG modules and reaction modules | |||
| Genomic information |
KO | Functional orthologs | ||
| GENES | Genes and proteins | |||
| GENOME | KEGG organisms and viruses | |||
| Chemical information |
COMPOUND | Metabolites and other chemical substances | ||
| GLYCAN | Glycans | |||
| REACTION RCLASS |
Biochemical reactions Reaction class |
|||
| ENZYME | Enzyme nomenclature | |||
| Health information |
Human information system |
NETWORK | Disease-related network variations | |
| VARIANT | Human gene variants | |||
| DISEASE | Human diseases | |||
| DRUG DGROUP |
Drugs Drug groups |
Health information category integrated with drug labels is called KEGG MEDICUS
These databases contain various data objects for computer representation of the biological systems. Thus, the database entry of each database is called the KEGG object, which is identified by the KEGG object identifier consisting of a database-dependent prefix and a five-digit number (see: KEGG objects).
| Release | Database | Object Identifier | Remark |
| 1995 | KEGG PATHWAY | map number | |
| KEGG GENES | locus_tag / GeneID | ||
| KEGG ENZYME | EC number | ||
| KEGG COMPOUND | C number | ||
| 1998 | KEGG REACTION | R number | |
| 2000 | KEGG GENOME | organism code / T number | |
| 2002 | KEGG ORTHOLOGY | K number | Ortholog IDs in 2000 |
| 2003 | KEGG GLYCAN | G number | |
| 2004 | KEGG RPAIR | RP number | Discontinued in 2016 |
| 2005 | KEGG BRITE | br number | |
| KEGG DRUG | D number | ||
| 2006 | KEGG MODULE | M number | |
| 2008 | KEGG DISEASE | H number | |
| 2010 | KEGG RCLASS | RC number | |
| KEGG EDRUG | E number | Renamed to ENVIRON | |
| 2011 | KEGG ENVIRON | E number | Discontinued in 2021 |
| 2014 | KEGG DGROUP | DG number | |
| 2017 | KEGG NETWORK | N number / nt number | |
| KEGG VARIANT | GeneID+variant number |
3. KEGG Molecular Networks
The most unique data object in KEGG is the molecular networks -- molecular interaction, reaction and relation networks representing systemic functions of the cell and the organism. Experimental knowledge on such systemic functions is captured from literature and organized in the following forms:- Pathway map - in KEGG PATHWAY
- Brite hierarchy and table - in KEGG BRITE
- Membership (logical expression) - in KEGG MODULE
- Membership (simple list) - in KEGG DISEASE
In 1995 the concept of mapping was first introduced in KEGG for linking genomes to metabolic pathways (metabolic reconstruction) using the EC number. Once the EC numbers were assigned to enzyme genes in the genome, organism-specific pathways could be generated automatically by matching against the enzyme (EC number) networks of the KEGG reference metabolic pathways. The EC number is no longer used as an identifier in KEGG. The KEGG Orthology (KO) system is the basis for genome annotation and KEGG mapping.
| Period | Identifier | Reference knowledge | Assignment |
| 1995-1999 | EC number | Metabolic pathways | Domain based |
| 2000-2002 | Ortholog ID | Metabolic and regulatory pathways | Domain based |
| 2003- | KO | Pathways and BRITE hierarchies | Gene based |
From a different perspective, individual instances of genes are grouped into KO entries representing functional orthologs in the molecular networks. There are two more types of such generalization in KEGG as shown below.
| Network type | Class | Instance |
| All types | KO (gene ortholog) | Genes in KEGG GENES |
| Biochemical reaction | RC (reaction class) | Reactions in KEGG REACTION |
| Drug interaction | DG (drug group) | Drugs in KEGG DRUG |
4. Network Variants
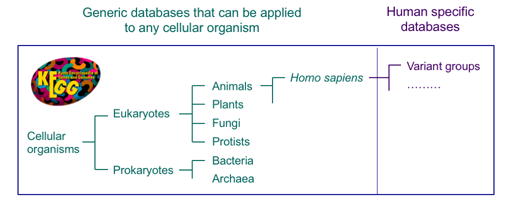
The KEGG database has been developed by focusing on conservation and variation of genes and genomes among different organisms. The reference datasets of KEGG pathway maps, BRITE hierarchies and KEGG modules have been developed with the concept of functional orthologs (KOs), so that KEGG pathway mapping and other procedures can be applied to any cellular organism.
References
- Kanehisa, M.; Toward pathway engineering: a new database of genetic and molecular pathways. Science & Technology Japan, No. 59, pp. 34-38 (1996). [pdf]
- Kanehisa, M.; A database for post-genome analysis. Trends Genet. 13, 375-376 (1997). [pubmed] [doi]
- Ogata, H., Goto, S., Sato, K., Fujibuchi, W., Bono, H., and Kanehisa, M.; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 27, 29-34 (1999). [pubmed] [doi]
- Kanehisa, M. and Goto, S.; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 27-30 (2000). [pubmed] [doi]
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Kawashima, S., and Nakaya, A.; The KEGG databases at GenomeNet. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 42-46 (2002). [pubmed] [doi]
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Kawashima, S., Okuno, Y., and Hattori, M.; The KEGG resources for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, D277-D280 (2004). [pubmed] [doi]
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Hattori, M., Aoki-Kinoshita, K.F., Itoh, M., Kawashima, S., Katayama, T., Araki, M., and Hirakawa, M.; From genomics to chemical genomics: new developments in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, D354-357 (2006). [pubmed] [doi]
- Kanehisa, M., Araki, M., Goto, S., Hattori, M., Hirakawa, M., Itoh, M., Katayama, T., Kawashima, S., Okuda, S., Tokimatsu, T., and Yamanishi, Y.; KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, D480-D484 (2008). [pubmed] [doi]
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M., and Hirakawa, M.; KEGG for representation and analysis of molecular networks involving diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, D355-D360 (2010). [pubmed] [doi]
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., and Tanabe, M.; KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, D109-D114 (2012). [pubmed] [doi]
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Kawashima, M., Furumichi, M., and Tanabe, M.; Data, information, knowledge and principle: back to metabolism in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, D199–D205 (2014). [pubmed] [doi]
- Kanehisa, M., Sato, Y., Kawashima, M., Furumichi, M., and Tanabe, M.; KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, D457-D462 (2016). [pubmed] [doi]
- Kanehisa, Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M., Sato, Y., and Morishima, K.; KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, D353-D361 (2017). [pubmed] [doi]
- Kanehisa, M., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., Morishima, K., and Tanabe, M.; New approach for understanding genome variations in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, D590-D595 (2019). [pubmed] [doi]
- Kanehisa, M; Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci. 28, 1947-1951 (2019). [pubmed] [doi]
- Kanehisa, M., Furumichi, M., Sato, Y., Ishiguro-Watanabe, M., and Tanabe, M.; KEGG: integrating viruses and cellular organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, D545-D551 (2021). [pubmed] [doi]
- Kanehisa, M., Furumichi, M., Sato, Y., Kawashima, M. and Ishiguro-Watanabe, M.; KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, D587-D592 (2023). [pubmed] [doi]
- Kanehisa, M., Furumichi, M., Sato, Y., Matsuura, Y. and Ishiguro-Watanabe, M.; KEGG: biological systems database as a model of the real world. Nucleic Acids Res. 53, D672-D677 (2025). [pubmed] [doi]
Last updated: November 1, 2025
